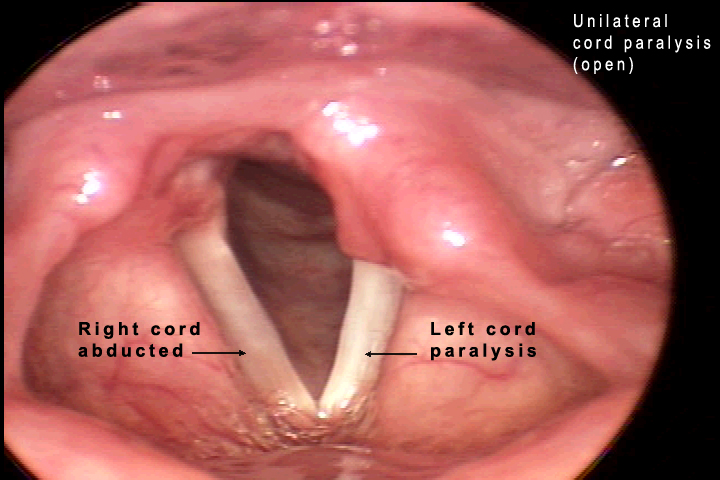
LEFT VOCAL CORD PALSY
Surgical anatomy: The left recurrent laryngeal nerve travels a similar course to the right except that it travels deep into the thorax. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve is situated more deeply in the tracheo-oesophageal groove and medial to branches of the inferior thyroid arteries. It arises on the anterior surface of the arch of aorta.
Aetiology:
- Usually seen in adults.
- Sex: Both sexes are equally affected.
Causes:
In the neck
- Accidental trauma.
- Benign thyroid disease.
- Malignant thyroid disease.
- Thyroid surgery.
- Carcinoma of cervical oesophagus.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy.
- Radical neck dissection.
In Mediastinum
- Bronchogenic carcinoma.
- Cancer of thoracic oesophagus.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
- Enlarged left auricle.
- Intrathoracic surgery.
- Idiopathic.
- Thoracic surgery.
- Metastatic lymph nodes.
- Bullet wounds.
- Pneumonectomy.
- Scalene node biopsy.
Carcinoma bronchus is an important cause of left recurrent paralysis and should always be excluded by HRCT chest, bronchoscopy and biopsy unless any other cause is obvious.
Clinical features:
- The voice of the patient may be slightly hoarse or unaffected.
- Respiration and swallowing are normal. Some patients get cough on quick ingestion of fluids.
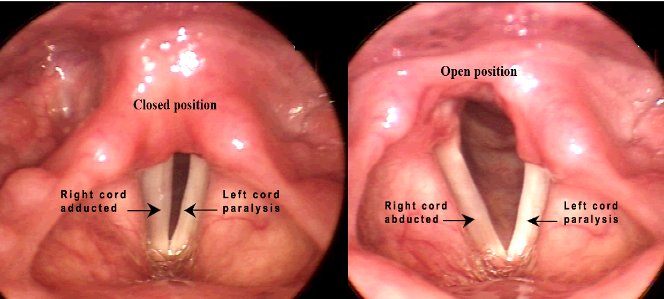
- On indirect laryngoscopy, the vocal cords maybe in median or paramedian position depending if the patient has unilateral abductor cord palsy or unilateral abductor and adductor cord palsy.
- Stroboscopy is done to confirm the exact position of the vocal cords and any local lesions.
Investigations:
- Routine blood investigations including ESR.
- CT Scan to detect intracranial lesions, mediastinal lesions and chest lesions.
- VDRL for syphilis.
- X-ray chest for mediastinal lesions, tuberculosis and aortic aneurysms.
- Barium swallow for oesophageal malignancy.
- Panendoscopy: This includes direct laryngoscopy, oesophagoscopy, bronchoscopy and sinoscopy to detect a malignancy.
- Fine needle aspiration cytology: Done to diagnose the type of tumour especially in neck masses and thyroid tumours.
- CT guided FNAC tests are also done for deep situated lesions.
Treatment:
- Treat the specific cause if any.
- If patient asymptomatic no treatment is required.
- Speech therapy to improve the voice.
Surgical:
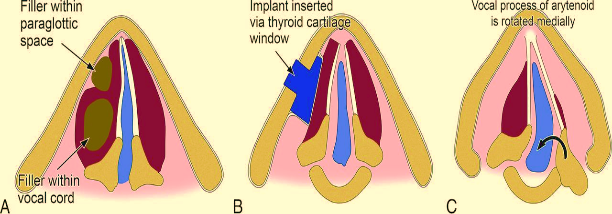
Cord medialization procedures:
- Teflon paste is injected over the paralysed cord to push it medially. This is done by microlaryngoscopy.
- Thyroplasty: The paralysed vocal cord is medialised by silastic implant.
- Vocal process of the arytenoid is rotated medially.
We Are Always Ready to Help You.
Book An Appointment

