
BRAINSTEM EVOKED RESPONSE AUDIOMETRY (BERA)
Definition: Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA) is an objective electrophysiological test measuring response in the brain waves that are stimulated by a clicking sound to check the central auditory pathways (hearing) of the brainstem.
It is a non-invasive technique to find the integrity of central auditory pathways through the VIIIth nerve, pons and midbrain.
Indications:
- Nervous system abnormalities.
- Children with hearing loss.
- To assess neurological functions.
- Malingering patients.
- Suspected acoustic neuroma.
- Central pontine myelinolysis.
- The test is done in an air-conditioned room.
- Patient is asked to wash the hair the night before the test.
- Patient in lying down position, eyes closed and preferably asleep.
- Infants and small children need to be administered sedatives like triclofos sodium in a
- dose of 50 mg per kg of body weight or promethazine hydrochloride in a dose of 0.5mg per kg of body weight so that the child is deeply sedated during the test.
- Electrodes are placed on the patient’s scalp, along the vertex and on each earlobe.
- Earphones are put on the ear. The patient hears a clicking sound between 10 and 40 clicks per second through the earphones.
- The electrodes pick up the brain’s response and record it on the graph.
- It measures hearing sensitivity in the range of 1000–4000 Hz.
- In a normal person, seven waves are produced in the first 10 ms.
- The first, third and fifth waves are most stable and are used in measurements.
- The waves are studied for absolute latency, inter-wave latency (usually between wave I and V) and the amplitude.
- Wave V is the most reliable and easily identifiable wave in the BERA tracing.
BERA waves Interpretation
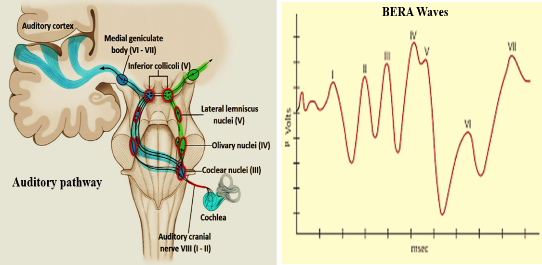
A series of waves are recorded in BERA test. These waves arise from:
- Wave I Distal part of CN VIII
- Wave II Proximal part of CN VIII near the brainstem
- Wave III Cochlear nucleus
- Wave IV Superior olivary complex
- Wave V Lateral lemniscus
- Waves VI Inferior colliculus
- Waves VII Medial geniculate body
Absolute latency:
Interwave latency:
| Wave I | 1.55- 1.75 millisecond |
| Wave III | 3.8 millisecond |
| Wave IV | 5.5- 5.85 millisecond |
| Interwave latency | Normal value (milliseconds) | Criteria for abnormality (milliseconds) |
| I-V | 4 | More than 4.4 |
| III-V | 2 | More than 2.4 |
| I-III | 2 | More than 2.4 |
Interaural latency:
| Parameter measured | Normal value (milliseconds) | Criteria for abnormality (milliseconds) |
| Interaural latency difference of wave V | Less than 0.3 | More than 0.3 |
This test has minimal discomfort and there are no risks involved.
Abnormal test results are indicative of:
1) Hearing loss.
2) Multiple sclerosis.
3) Cerebrovascular accidents (stroke).
We Are Always Ready to Help You.
Book An Appointment

