CALDWELL LUC SURGERY
Introduction: It is a surgical opening made on the anterior wall of the maxilla via the canine fossa to visualize and remove disease from the maxillary sinus. This operation is followed by an intranasal antrostomy.
George Caldwell in New York and Henri Luc in France described this operation simultaneously more than 100 years ago.
Indications:
- Recurrent Antrochoanal polyp in patient above 16 years.
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis not responding to 3 antral punctures.
- Removal of foreign bodies or root of a tooth.
- Removal of Dentigerous cyst.
- Closure of Oroantral fistula.
- Inspection and biopsy of antral malignancy.
- Orbital decompression.
- Elevation and stabilization of orbital floor fractures.
- As an approach to ethmoids (Horgan’s transantral ethmoidectomy).
- Approach to pterygopalatine fossa for ligation of maxillary artery.
- Vidian neurectomy.
- Treatment of Atrophic Rhinitis:a) Raghav Sharan’s operation: Implantation of maxillary sinus mucosa in the nasal cavity. b) Whitmack’s operation: Implantation of the Stenson’s duct (parotid duct) into the maxillary antrum.
- Implantation of radium needles in the maxillary antrum in case of malignancy of the maxilla.
Contraindications:
- Not done below 15 years of age as dentition and growth of middle third of face is incomplete.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertension.
- Acute sinusitis can cause excessive bleeding.
Complications:
Procedure:
Anesthesia: General Anesthesia with cuffed endotracheal tube and throat pack is given around the tube to prevent aspiration of blood. Position:
| Immediate | Late |
|
|
Anesthesia: General Anesthesia with cuffed endotracheal tube and throat pack is given around the tube to prevent aspiration of blood. Position:
Patient is in supine position with head end slightly raised.
Steps:
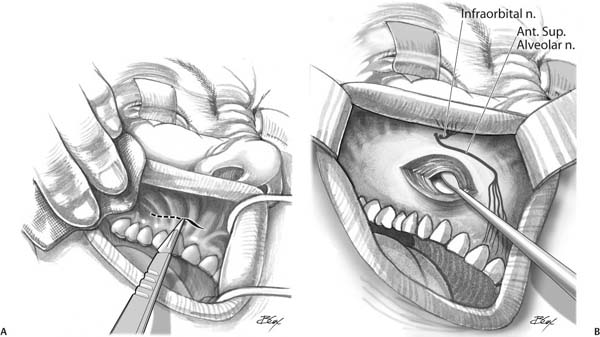
- Infiltration with normal saline and adrenaline in 1:1,00,000, submucosally helps in reducing bleeding. Horizontal incision is made in the gingivolabial sulcus up-to the second molar through the mucous membrane and periosteum.
- Mucoperiosteal flap is raised from the canine fossa avoiding injury to infraorbital nerve.
- Using an electric burr or gouge and hammer an opening 1.5 cm is made in the region of the canine fossa over the anterior wall of the maxillary antrum.
- Antral opening is enlarged by punch forceps. Diseased antral mucosa and the pathology in the maxillary antrum is removed using curette and forceps. A sinus endoscope can also be inspected in sinus to inspect the sinus.
- An intranasal antrostomy is done by pushing a hemostat into the antrum from inferior turbinate. The edge of this opening is smoothened.
- Maxillary sinus is packed with ribbon gauze dipped in liquid paraffin and antiseptic cream.
- Mucosal incision is sutured by absorbable material like catgut or vicryl. Post operatively the nasal pack is removed after 24-48 hours.
We Are Always Ready to Help You.
Book An Appointment

