TONSILLITIS
Infection of the tonsils is one of the most common pathology in the oral cavity. Depending on the time period and recurrence of the infection, tonsillitis is divided into:
- Ingestion of cold or infected food stuff.
- Low immunity and resistance.
- Upper respiratory tract infection.
- Pollution and ill-ventilated environment.
- Close contact with infected persons.
- Residual tonsillar tissue left post-tonsillectomy.
- Acute catarrhal or superficial tonsillitis: It is mostly seen in viral infections. Here tonsillitis is a part of generalized pharyngitis.
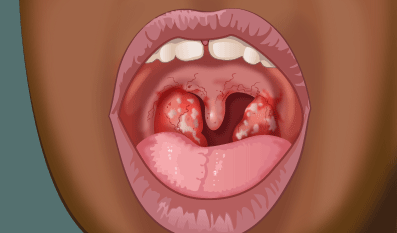
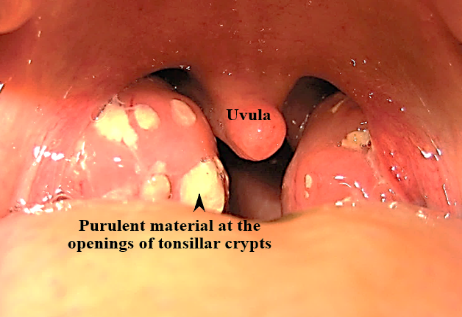
- Acute follicular tonsillitis. Here infection spreads into the crypts. Purulent material presents at the openings of crypts as yellowish spots.
3. Acute parenchymatous tonsillitis. Here tonsil substance is affected. Tonsil is uniformly enlarged and red.

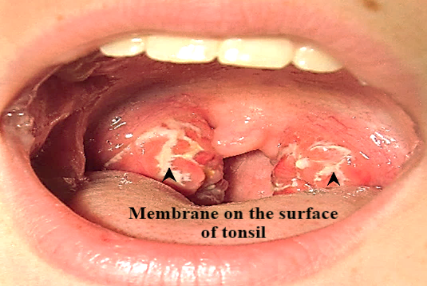
4. Acute membranous tonsillitis. It is a after acute follicular tonsillitis when exudation from the crypts coalesces to form a membrane on the surface of tonsil.
- Throat pain is acute, especially on swallowing.
- High grade fever, malaise with tachycardia.
- Enlarged and tender jugulodigastric lymph nodes.
- Voice may be changed due to accumulation of saliva.
- Referred pain to the ear via the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Both tonsils are congested and swollen with accumulation of pus in the tonsillar crypts.
- Pharyngitis is usually present.
- Foul breath may be present.
- Movement of the soft palate and tongue are restricted due to pain.
Treatment:
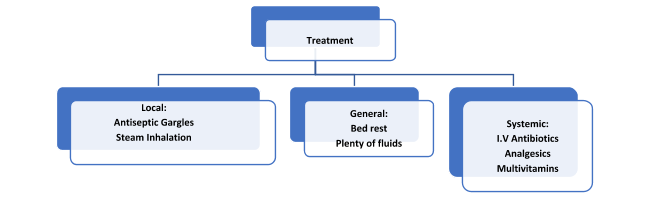
- Patient is advised rest with good fluid intake.
- Analgesics (aspirin or paracetamol) are given according to the age of the patient in order to relieve local pain and bring down the fever.
- Antimicrobial therapy- Most of the infections are due to Streptococcus so previously penicillin was given. Patients allergic to penicillin were treated with erythromycin. With the advent of newer antibiotics, Amoxicillin trihydrate and Potassium clavulanate (clavulanic acid) is the antibiotic of choice for treatment of tonsillitis. Antibiotics should be continued for 7–10 days.
Complications of Acute tonsillitis:
- Quinsy (peritonsillar abscess).
- Parapharyngeal abscess.
- Respiratory obstruction.
- Septicemia.
- Rarely mediastinitis due to rapid spread of infection in the neck.
II. Chronic Tonsillitis: Chronic tonsillitis is caused by recurrent attacks of acute tonsillitis.
Aetiology:
Age: Children are most commonly affected; however, it occurs in adults as well.
Sex: Both sexes are equally affected.
Predisposing factors:
- Ingestion of cold or infected food stuff.
- Low immunity and resistance.
- Upper respiratory tract infection.
- Pollution and ill-ventilated environment.
- Close contact with infected persons.
- Residual tonsillar tissue left post-tonsillectomy.
Symptoms:
- Recurrent throat pain, fever.
- Recurrent upper respiratory tract infection.
- Enlarged Cervical lymph nodes.
Signs:
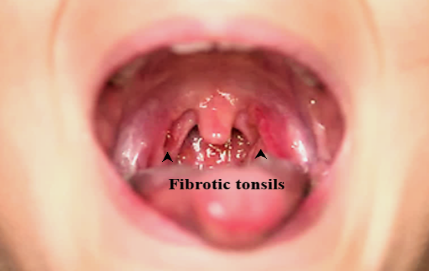
- Tonsils are hypertrophied and fibrotic.
- On pressing the tonsil, cheesy material can be seen.
- Enlarged, nontender, jugulodigastric lymph nodes.
Treatment:
- Nutritious and high protein diet.
- Treatment of coexistent infection of teeth, nose and sinuses.
- Antibiotics, analgesics, antiseptic gargles
- Tonsillectomy should be done when tonsils interfere with speech, deglutition and respiration or cause recurrent attacks.
We Are Always Ready to Help You.
Book An Appointment

