ENT Specialist In Mumbai
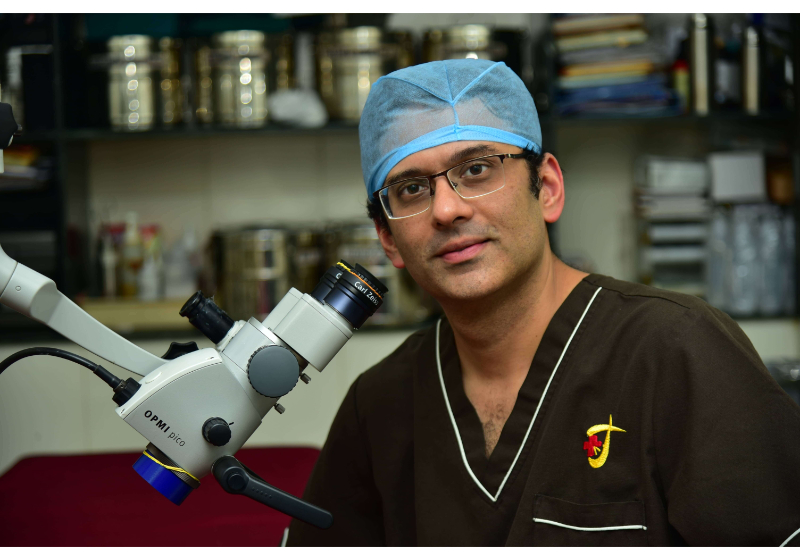
Dr. Meenesh Juvekar
M.S (ENT), D.N.B, D.O.R.L, M.N.A.M.S
Trustee Tara Foundation



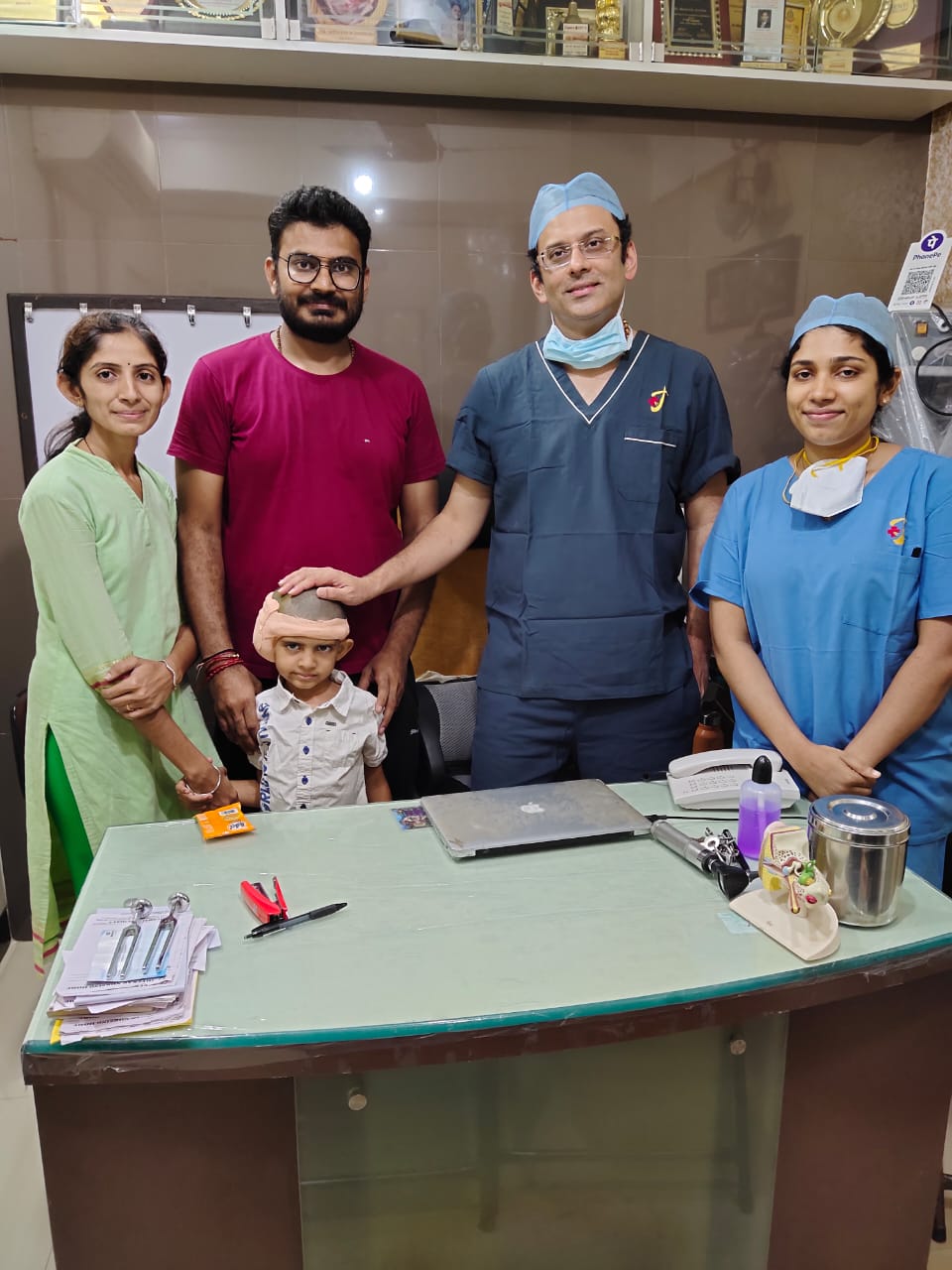
Best Cochlear Implant Surgeon in Mumbai
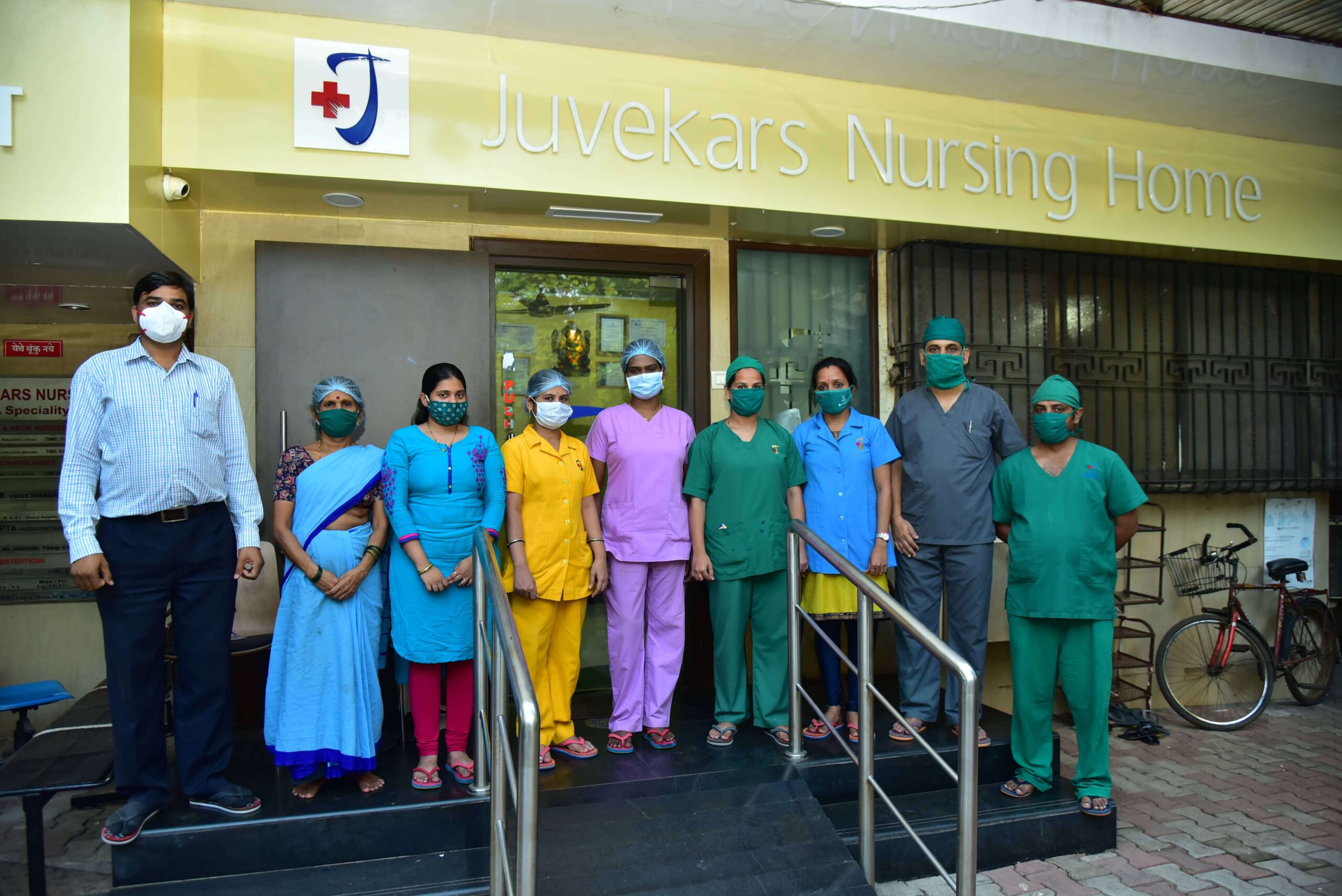

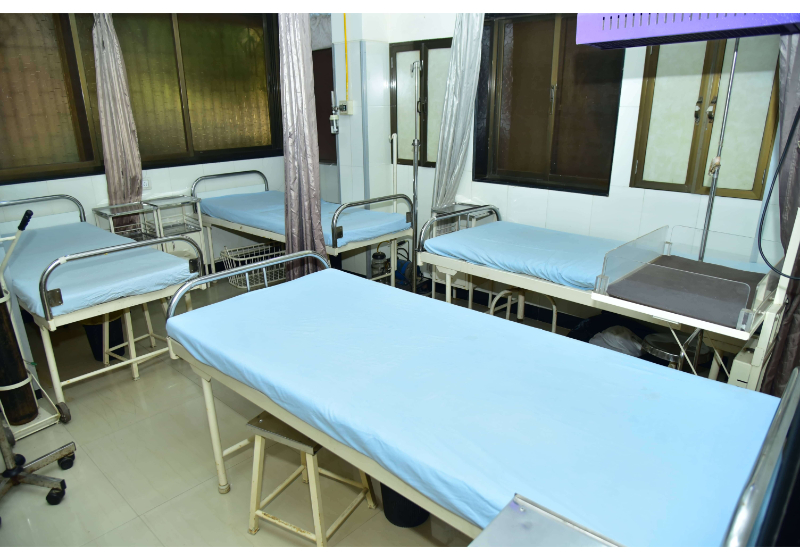
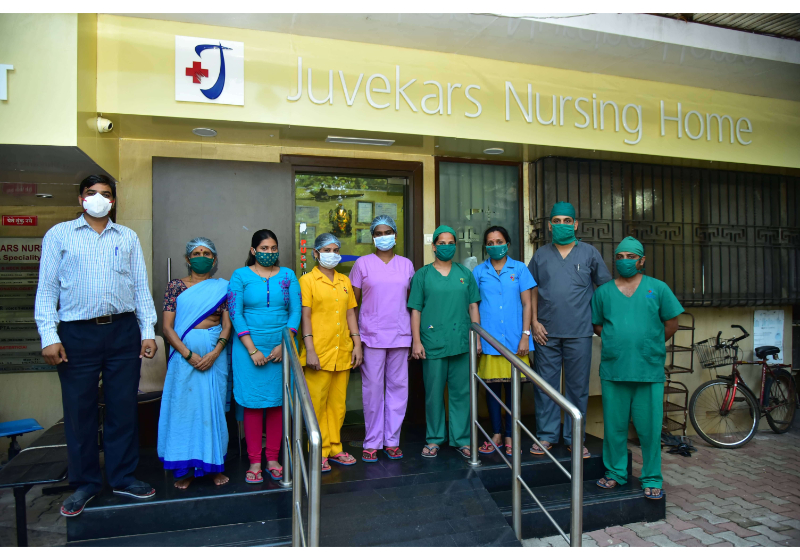
About Juvekars Nursing Home
Juvekars Nursing Home has round the clock ECG facilities. Laboratory services comprise of Microbiology, Biochemistry, Clinical Pathology, Hematology and Serology which are all essential for IPD patients as well as OPD patients. The department is open to receive samples round the clock. Histopathological studies are also carried out. Sonography (USG) facility is also part of the diagnostic services offered at Juvekars Nursing Home.
“Our profession is the only one which works unceasingly to annihilate itself.”
ENT Doctor In Mumbai

Dr. Meenesh Juvekar
M.S (ENT), D.N.B, D.O.R.L, M.N.A.M.S
Trustee Tara Foundation
testimonial Videos
Specialist ENT Media Coverage



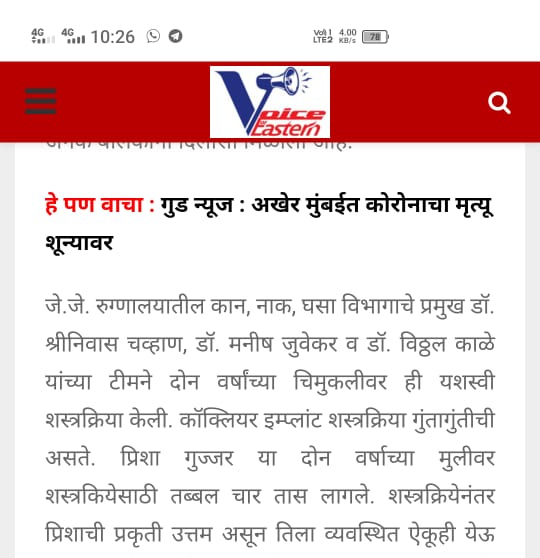



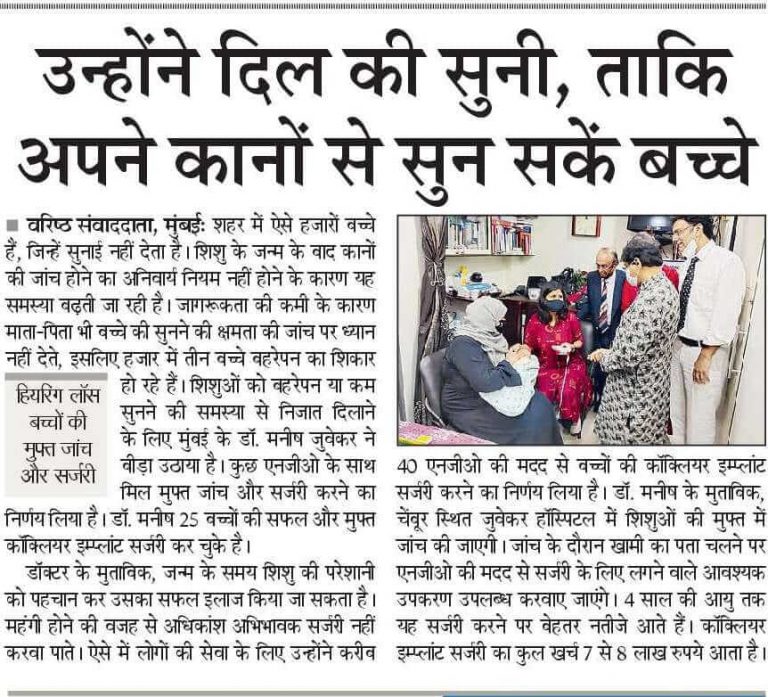






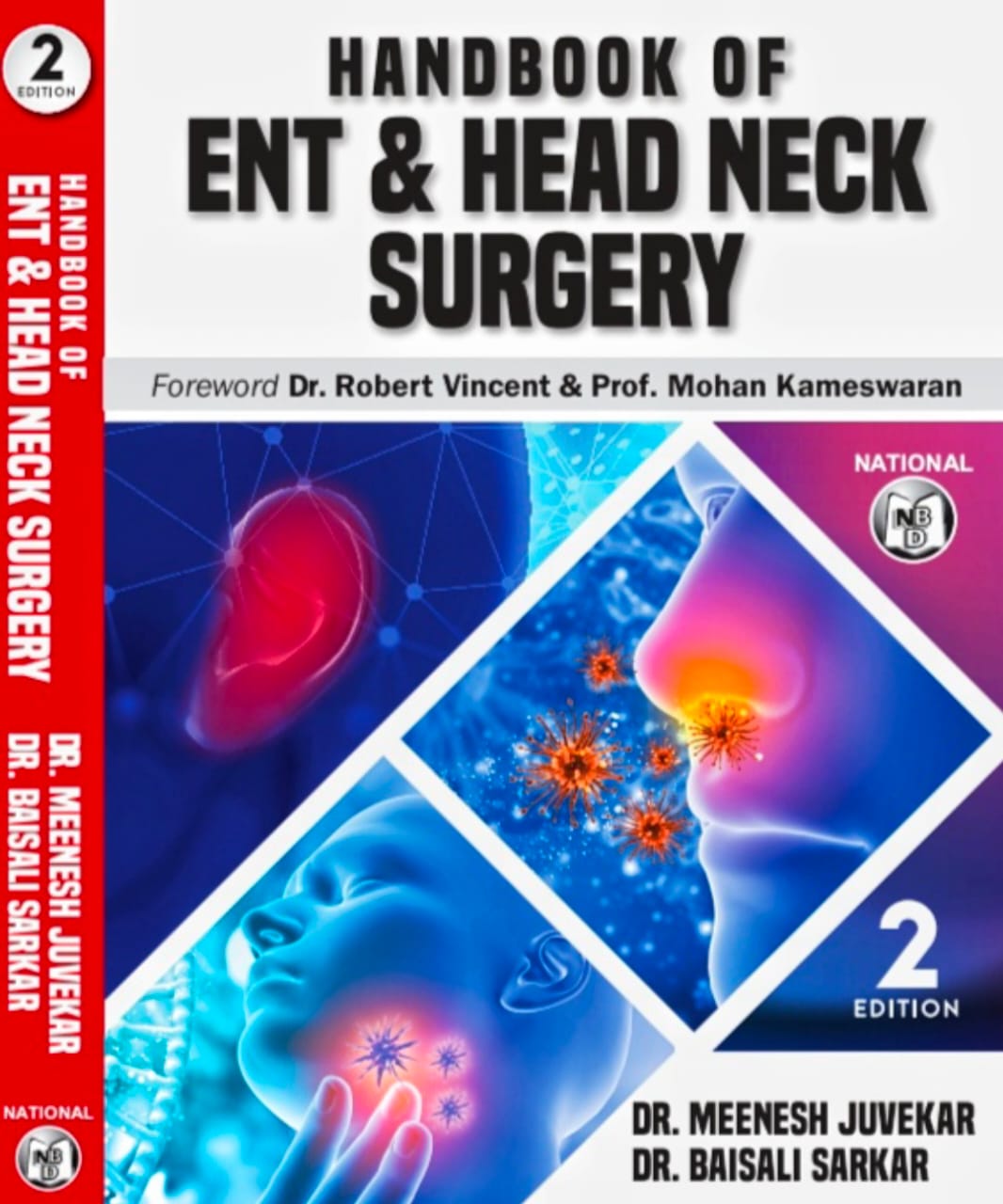
Our Publications
Author: Dr. Meenesh Juvekar
ENT Doctor in Mumbai

4.3/5
1860 Reviews
5/5
Practo 1630 Reviews
Our ENT Doctor Services

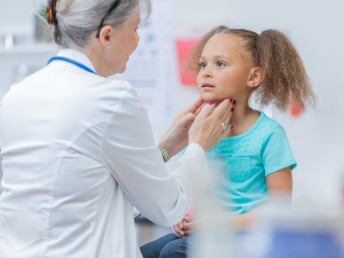
Ear
Ear problems are rampant today - be it infection, hearing loss, blocked ears, discharge from ears or other problems.
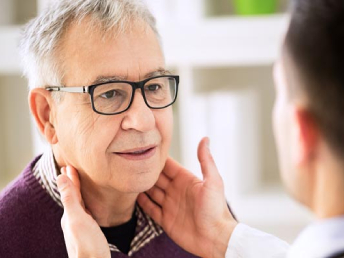
Nose
From innocuous common colds to nagging sinusitis to bothersome growths inside the nose (polyps), we have all seen …

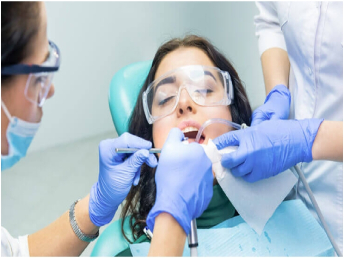
Throat
Almost every one of us has experience a sore throat, a squeaky voice or a trouble some cough some time in life.
Larynx
The larynx (/ˈlærɪŋks/), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound.
Oesophagus
The oesophagus is a muscular tube. It connects your mouth to your stomach. When you swallow food…
oral cavity and pharynx
The oral cavity includes the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks (buccal mucosa), the teeth, the gums, the front two-thirds of the tongue
Why People Trust Us
Juvekars Nursing Home is a well equipped hospital with several facilities. We provide Specialist ENT services in Chembur which lies in the eastern suburb of Mumbai. Juvekars Nursing Home has been steadily moving towards providing complete health care solutions to patients. We are amongst the Best Ent doctor in Mumbai
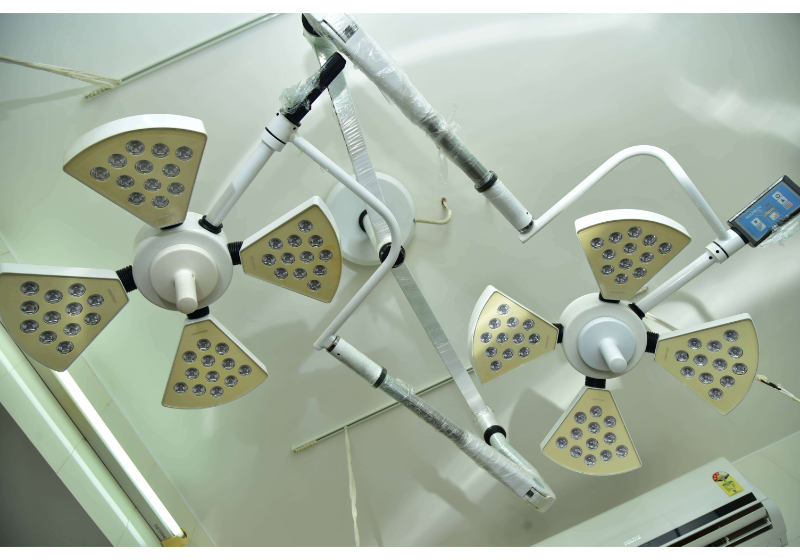
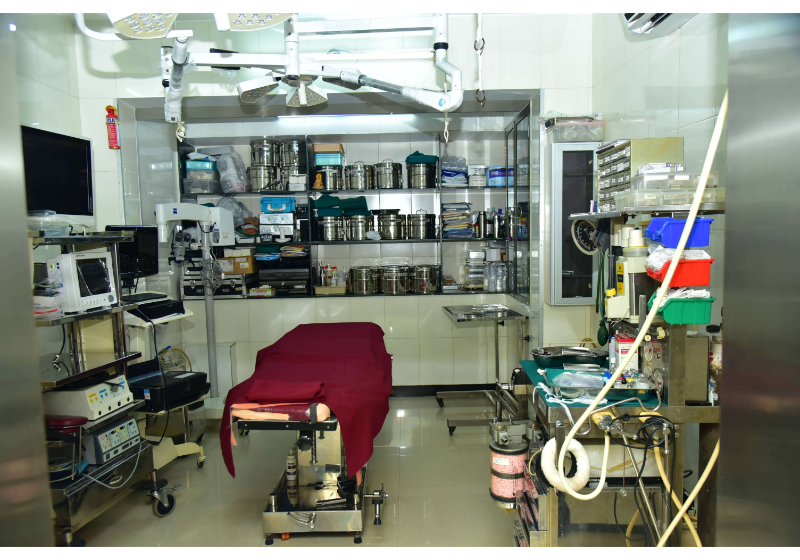
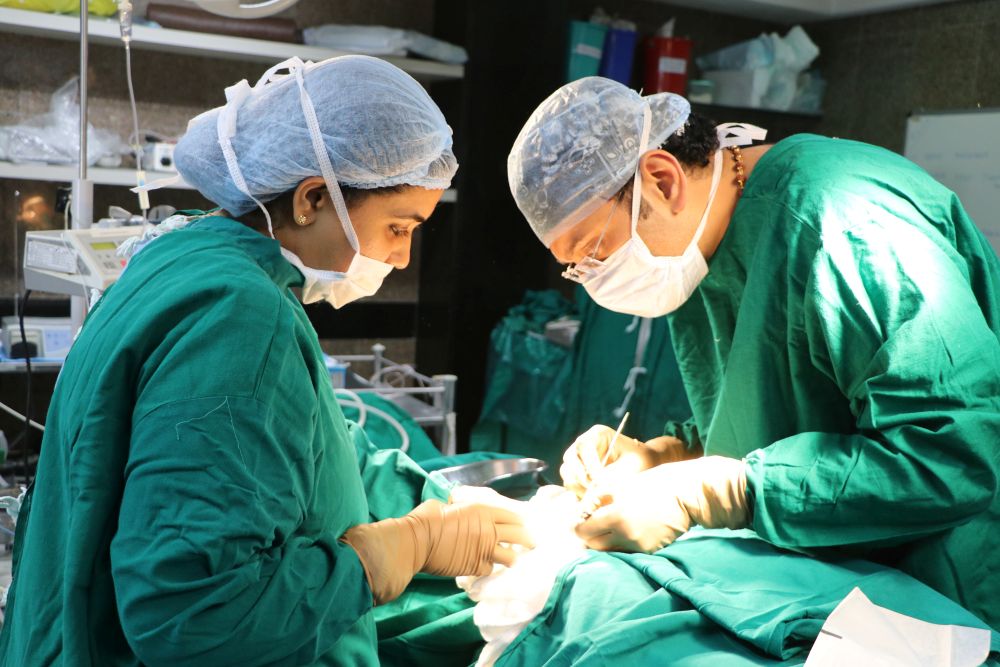
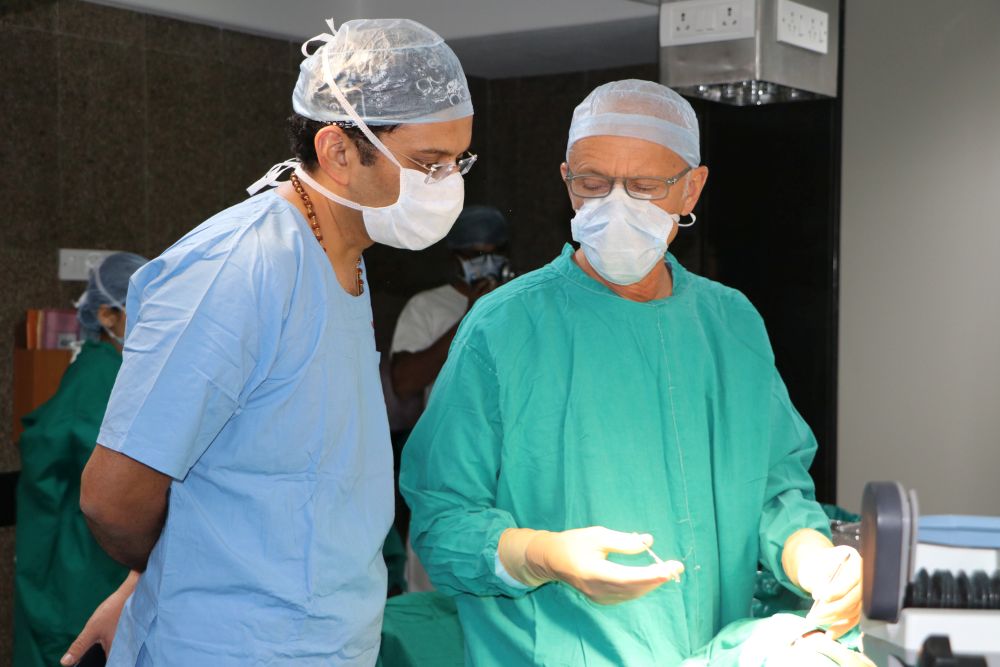
High Quality OT
Juvekars Nursing home has one of the most modern and well equipped Operation Theatres in Chembur, Mumbai. It is suited for all routine surgeries keeping in mind E.N.T Surgeries.We are one of the best specialist ent doctor in mumbai
Unmatched Expertise
We have best ent doctor in mumbai with excellent domain knowledge and with years of experience, they can provide best in class healthcare services.
Precise Result
We believe in providing the accurate results to the clients, according to our principals providing the best healthcare to the person in need is our primary duty. And that is why we are the best ent doctor in Mumbai since many years
Qualified Staff
We believe that each and every member in the team plays important role in helping out patients in recovering from there problem so we have best staff that can help our doctors as well as patients so that they can get relief and can live there happy life again
Some kind words from "Sonu Sood"!
What People Say About Us
Best ENT doctor in Mumbai
Aasifa Ruhani
ENT doctor near me



Our Pleasure
A large range of consultative, diagnostic and surgical services are provided to people whose health complaints do not warrant hospitalization. These OPD and Specialist ENT doctors are available from 9 am to 9 pm every day.

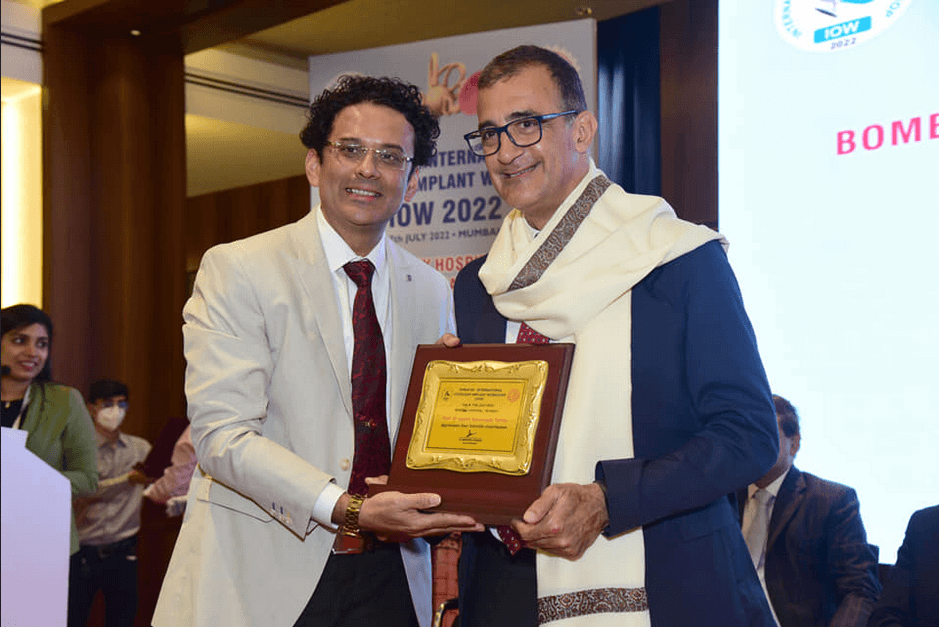
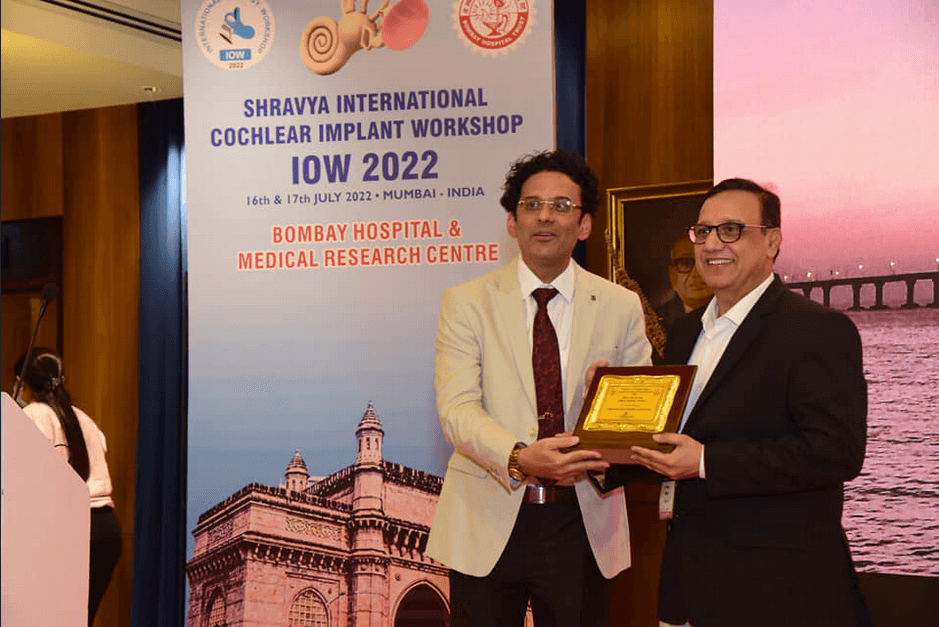
Our Workshop
Due to COVID-19 pandemic, the 4th International Otology Workshop (IOW) 2020 which was scheduled from 12 to 14 June 2020 is postponed. New dates will be announced shortly. We regret the inconvenience. Please stay indoors, stay safe and healthy with your family.
Get One Step Ahead Of Disease
The hospital has specially designed health check up plans to suit the needs of the patient. A group of dedicated, well qualified and experienced doctors provides a broad range of in-patient and out-patient health care services to match the needs of the community. The nurses and para-medical staff is also well qualified and trained to efficiently cater to the patients’ needs. We are the best Ent Doctor in Mumbai
ENT Doctor in Mumbai - Dr Meenesh Juvekar

Dr Meenesh Ravindra Juvekar is a ENT Doctor in Mumbai & renowned ENT Specialist Surgeon at Bombay Hospital Medical and Research Centre and Grant Medical College and J.J.
Service Type: ENT Doctor in Mumbai
ENT Doctor - Dr Meenesh Juvekar
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
ENT Doctor - Dr Meenesh Juvekar
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
ENT Doctor - Dr Meenesh Juvekar
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
ENT Doctor - Dr Meenesh Juvekar
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.